What is a Coronary Insulator?
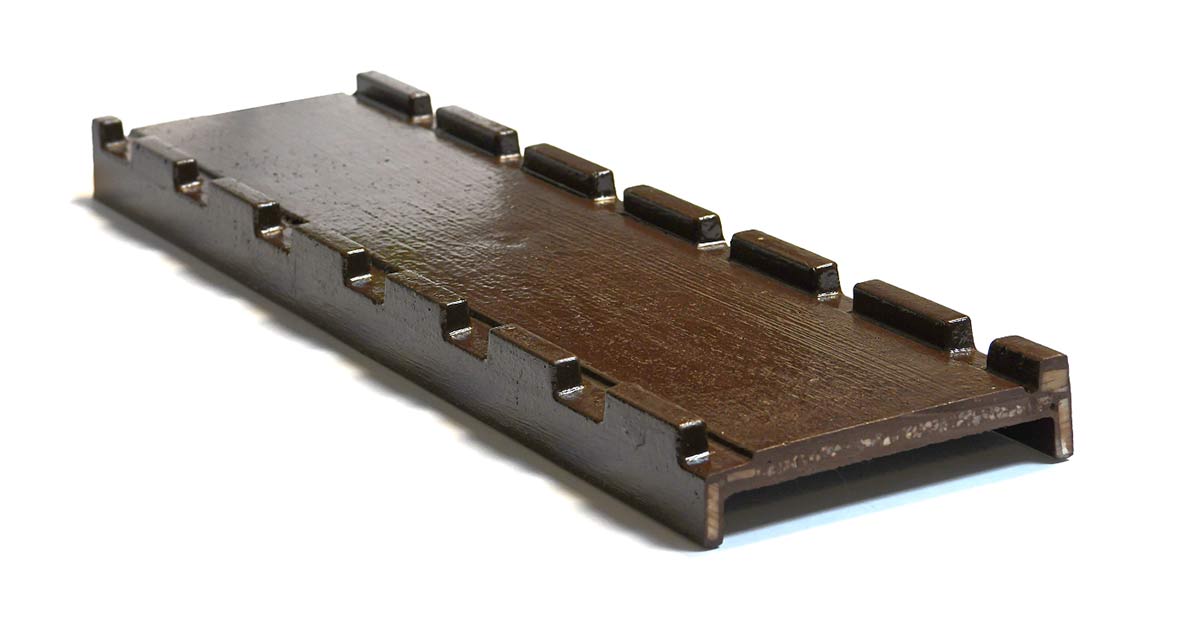

In the realm of copper and zinc refining, ensuring the utmost protection and efficiency of refinery cells is of paramount importance. A vital component that contributes to this goal is the coronary insulator. But what exactly is a coronary insulator, and how does it play a pivotal role in consistency of operations in refinery processes?
A coronary insulator is an innovative and specialized type of insulator to act as a secondary protective layer within refinery cells. Its primary purpose is to shield the cell against a multitude of potential threats, including chemical attacks, high heat concentrations, and the damaging effects of short circuits. By serving as a reliable barrier, these insulators enhance the structural integrity of cells, optimizing their performance and extending their operational lifespan.
In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate functionalities and applications of coronary insulators in copper and zinc refineries, exploring how they optimize processes and enhance the lifespan of critical equipment.
The Functionality of Coronary Insulators
Coronary insulators are specially designed to act as a robust barrier against harmful elements that can negatively impact cell structures. With their unique 90-degree edges, these insulators effectively resemble an umbrella, providing a shield against acid drops and redirecting electrolytes away from the cell. This redirection of electrolytes not only protects against corrosion but also ensures optimal alignment of the standard top insulator, reducing the risk of misalignment-induced issues.
Mitigating Thermal Stress and Preventing Short Circuits
One of the primary advantages of coronary insulators is their ability to combat thermal stress, a notorious source of cell damage in refineries. In the event of a major short circuit, the various layers of textiles in these insulators serve as a thermal barrier, preventing excessive heat generated by the short circuit from transferring to the cell body. By effectively limiting thermal stress, coronary insulators significantly enhance the structural integrity and longevity of cells, minimizing the need for frequent replacements.
Extending the Lifespan of Cracked Cells
Another remarkable aspect of coronary insulators is their ability to provide an extended lifespan to cells that may already have cracks or structural weaknesses. By reinforcing the cell’s protective layers, these insulators create a robust shield that prevents further deterioration due to the penetration of electrolyte, allowing the cells to continue functioning effectively and safely.
Ensuring Safety and Reliability
Safety is a paramount concern in any refinery setting. The implementation of coronary insulators bolsters safety measures by acting as a secondary line of defense against potential chemical attacks and thermal stress. The reliability of cell structures is critical for seamless refinery operations, and coronary insulators play a crucial role in safeguarding cell integrity.
Customized Solutions for Optimal Performance
The versatility of these insulators allows them to be customized to suit the specific needs of each copper and zinc refinery. Engineers can tailor the design and specifications of these insulators to optimize their performance based on the refinery’s unique operational requirements. This adaptability ensures that the insulators seamlessly integrate into existing cell structures, enhancing overall efficiency.
In conclusion, coronary insulators stand as a game-changing innovation in the world of copper and zinc refining. These specialized insulators provide a remarkable protection against chemical attacks, thermal stress, and short circuits, effectively safeguarding the structural integrity of cell components. With their ability to extend the lifespan of cracked cells and their versatile customization options, coronary insulators pave the way for optimized refinery processes and enhanced equipment longevity. Embracing this technology promises to revolutionize copper and zinc refineries, ensuring consistency of production rates and efficiency of operations for years to come.